A Low Spurious RF Signal Generator
Usage
The low spurious RF generator app is dependent on spur data as calculated using Analog's ADISimFrequencyPlanner. The ADISimFrequencyPlanner software and documentation can be downloaded from Analog's website.
App usage is:
python rfgen.py -h usage: rfgen.py [-h] [--nogui] [--no_cal_data] [-d DEVICE] [-b BAUDRATE] [-A IPADDR] [-P PORT] -D SPURDATA A low spurious RF signal generator. optional arguments: -h, --help show this help message and exit --nogui Disable GUI and run 'headless' --no_cal_data No output power calibration data should be used -d DEVICE, --device DEVICE The hardware serial device -b BAUDRATE, --baudrate BAUDRATE Baud rate (default: 0) -A IPADDR, --ipaddr IPADDR IP address for to bind the RPyC server instance -P PORT, --port PORT TCP port for the RPyC server instance -D SPURDATA, --spurdata SPURDATA File containing freq. planner spur data
Note that a spur data file is a required parameter specified using the -D
(--spurdata) command line parameter. A default spur data file
(spur-data.csv) is available with the reference design files.
Example command line invocation:
When the app first starts up most of the controls are inactive and greyed
out (See Figure 1a). Clicking the Initialize button will initialize the
hardware and make the app available for use (See Figure 1b).
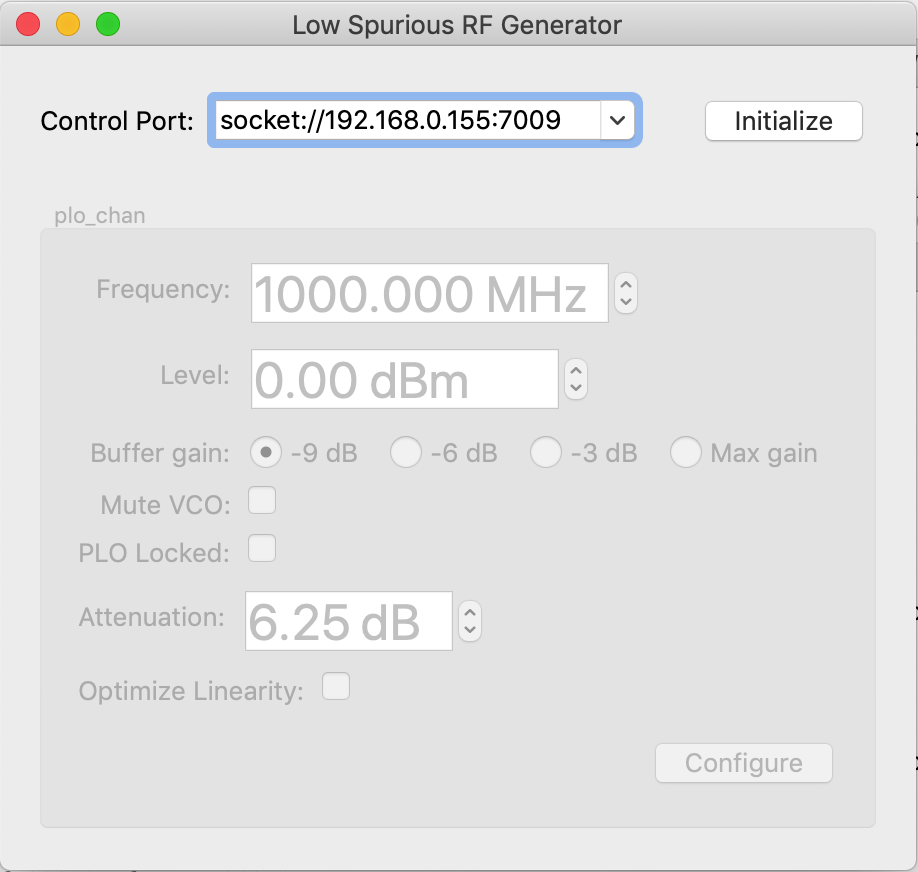
Figure 1a: Initial RF generator app window
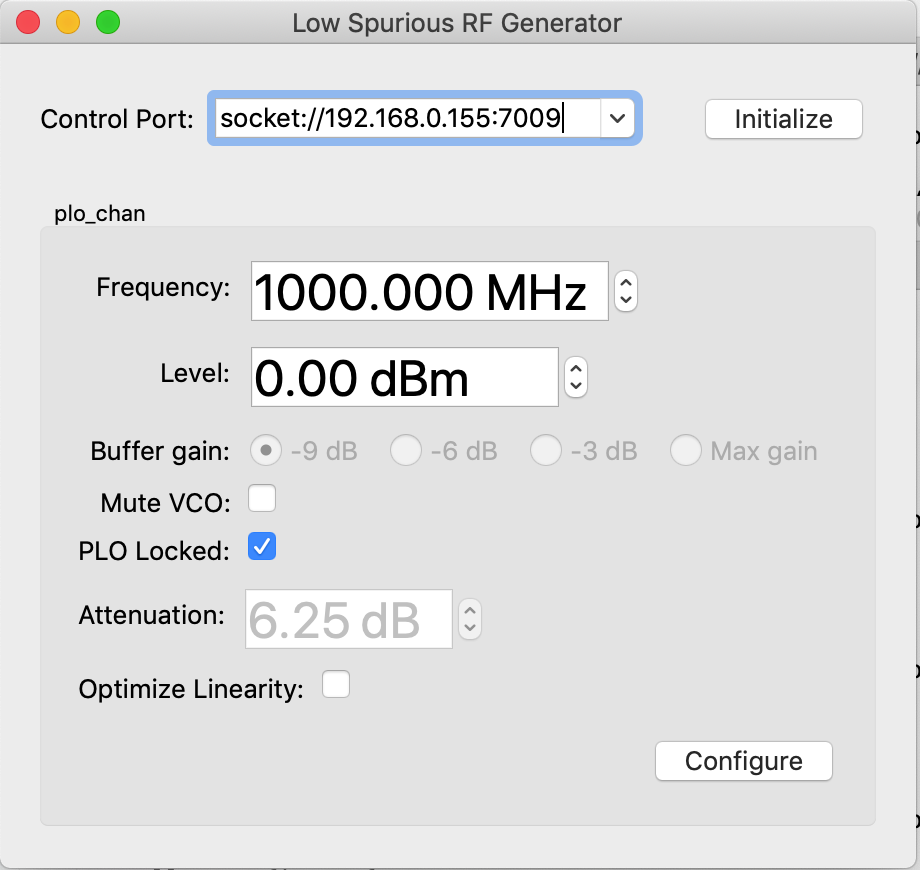
Figure 1b: RF generator app after initialization
The frequency and the level of the signal generator output are adjustable
using the associated controls. The Configure button is activated in order
to effect the settings in hardware. Updates to the hardware are reflected
in the read-only values of HMC833 buffer gain and the output attenuation.
Software control
Software control of the signal generator is done via the
LowSpurRFGenService RPyC service provided by the Low Spurious RfGen
reference design app. The service API is given here: The RFGenService.
Example rpyc client for the signal generator:
import rpyc rfgen = rpyc.connect("turing", 18867) rfgen.root.initialize() plo = rfgen.root.plo_chan plo.plo_ctl.freq = 1500.0 rfgen.root.configure_plo_freq() plo.plo_ctl.buffer_gain = int(hmc833.OutputBufferGain.MAXGAIN_MINUS_6DB) rfgen.root.configure_plo() plo.atten_ctl.attenuation = 0.0 rfgen.root.configure_atten() plo.plo_ctl.vco_mute = True rfgen.root.configure_plo() plo.plo_ctl.vco_mute = False rfgen.root.configure_plo() rfgen.close()
LowSpurRFGen service API
def initialize(self): """Initialize the service app and associated hardware modules. """ @property def plo_chan(self): """Return a reference to the signal generator channel object. :return: A ``PLOChan`` instance. .. code:: python rfgen = rpyc.connect('127.0.0.1', 18867) rfgen.root.initialize() plo = rfgen.root.plo_chan plo.plo_ctl.freq = 1500.0 rfgen.root.configure_plo_freq() """ def configure_plo_freq(self) -> bool: """Update the PLO module output frequency. .. code:: python rfgen = rpyc.connect('127.0.0.1', 18867) rfgen.root.initialize() plo = rfgen.root.plo_chan plo.plo_ctl.freq = 1500.0 lock_status = rfgen.root.configure_plo_freq() """ def configure_plo(self) -> bool: """Update the PLO module hardware. .. code:: python rfgen = rpyc.connect('127.0.0.1', 18867) rfgen.root.initialize() plo = rfgen.root.plo_chan plo.plo_ctl.buffer_gain = \ hmc833.OutputBufferGain.MAXGAIN_MINUS_6DB lock_status = rfgen.root.configure_plo() """ def configure_atten(self): """Update step attenuator module hardware. .. code:: python rfgen = rpyc.connect('127.0.0.1', 18867) rfgen.root.initialize() plo = rfgen.root.plo_chan plo.atten_ctl.attenuation = 10.0 rfgen.root.configure_atten() """ def configure(self) -> bool: """Update the channel hardware - PLO and attenuator. """ def set_calibration_mode(self, mode): """Set the calibration mode. :param mode: True to set the app to calibration mode, False to set the app for normal operation. :type mode: bool Setting the calibration mode to True will disconnect the HMC833 controller ``freq_changed`` signal. This then prevents the ``_update_channel_settings`` method being invoked which in turn prevents any change to the channel attenuation. .. code:: python rfgen = rpyc.connect('127.0.0.1', 18864) rfgen.root.initialize() rfgen.root.set_calibration_mode(True) """
Design Notes
Figure 2a: Spur comparison at 2000.1 MHz.
Figure 2b: Spur comparison at 3900.4 MHz.
Figure 3: RF generator schematic design.
Assembly
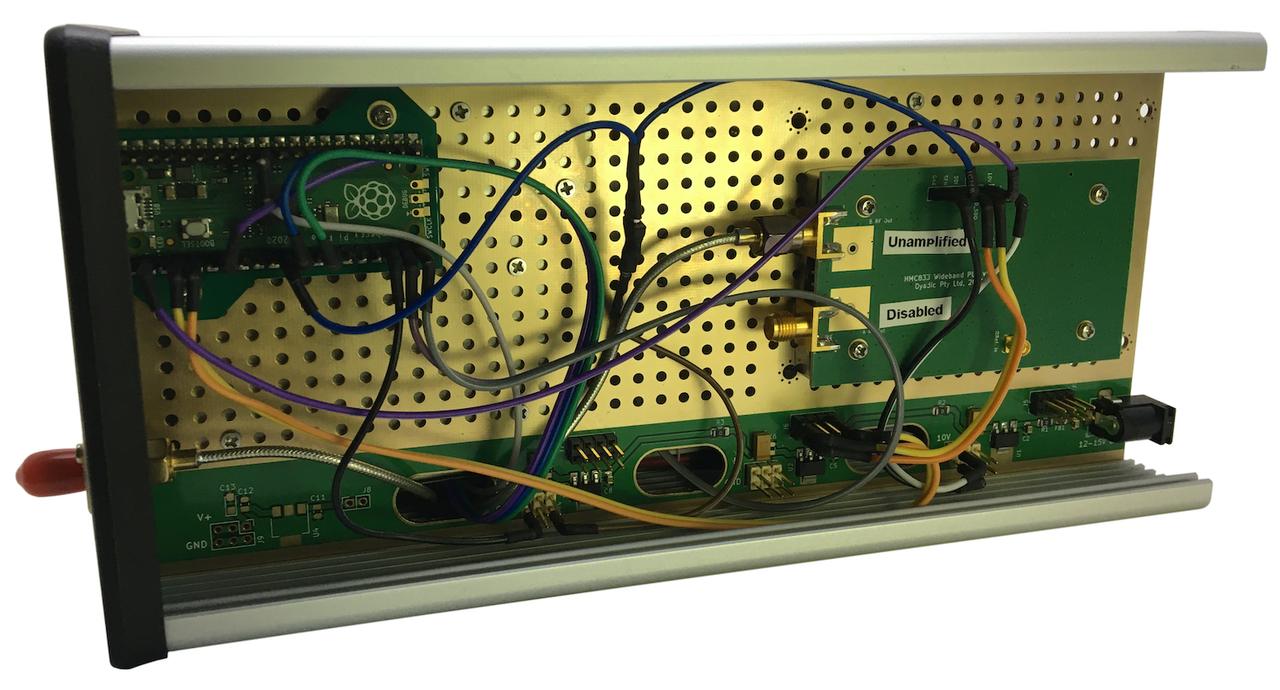
Figure 4a: Top side of assembly.
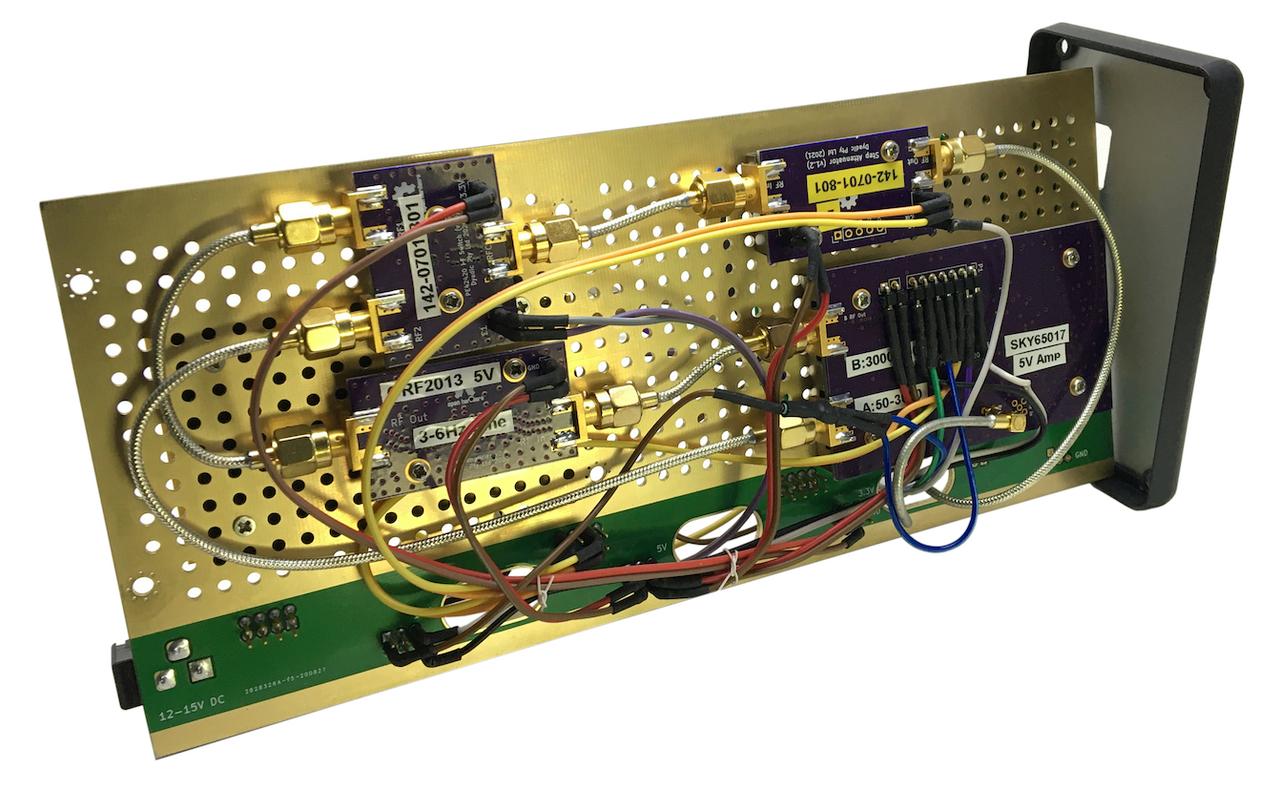
Figure 4b: Reverse side of assembly.
Calibration
For a specified frequency the output power for the signal generator is determined by setting the buffer gain value of the PLO module together with a step attenuation value. In order to determine the correct buffer gain value the power level generated by the associated PLO module must have been measured before hand. This is done using the calibration process described here.
Applying calibration data
Calibration measurements are contained in one set of dictionaries for each of the signal generator channels.
Measuring calibration data
Calibration measurements are made using the dual channel power meter. Because of this, the measured power levels will be the integrated power of the output signal. This will include the power in any harmonics present in the signal as well as the integrated noise out to the bandwidth of the power detector. The synthesizer has a low noise floor (typically -160 dBm) and therefore the integrated noise is negligible in this application. For low frequencies (< 500MHz) an appreciable amount of harmonic power is present. Depending on the application this may need to be corrected for when the signal generator is in use.
The RFBLOCKS_REFDESIGNS environment variable needs to be set to the
directory which holds the local rfblocks reference design git repos. This
value of this environment variable is used to find the dual power meter
app. It takes about an hour to complete a calibration measurement run.
Figure 5a: RF signal generator calibration setup schematic.
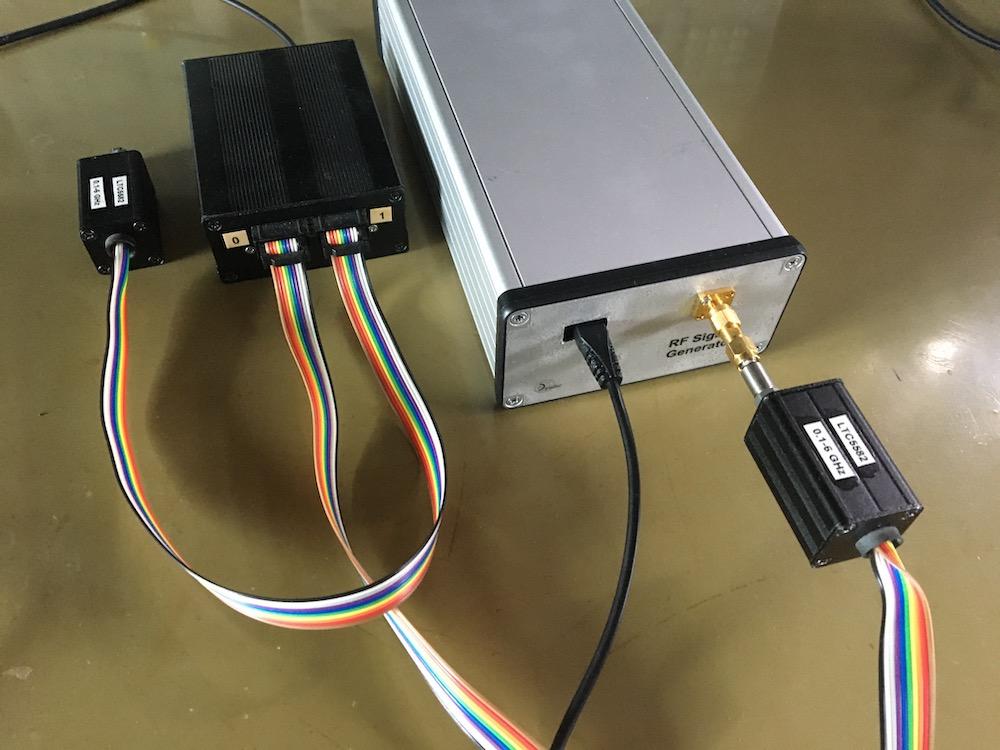
Figure 5b: RF signal generator calibration physical setup.
The Signal Generator App Source Code
A full description and code for the signal generator app is given here: rfgen.py.
Scripts
Output power calibration
-
Output power calibration script.
-
Initialize signal generator
try: rfgen = rpyc.connect("127.0.0.1", 18867) except ConnectionRefusedError: print("Can't connect to the rfgen app. Is it running?") sys.exit(-1) rfgen.root.initialize() plo = rfgen.root.plo_chan plo.atten_ctl.attenuation = 0.0 rfgen.root.configure_atten() plo.plo_ctl.vco_mute = False rfgen.root.set_calibration_mode(True)
-
Initialize the power meter. Note that a 24 dB attenuator are connected between the RF generator signal output and the power meter measurement head. A calibration data file for this attenuator (generated separately) is loaded explicitly.
pwr_app_path = Path( os.path.expandvars('${RFBLOCKS_REFDESIGNS}/PowerMeter/app')) # The power meter is set up with measurement head 'Det 3' (on power # meter channel 0) connected to RF generator output via the # 48-0007 24 dB attenuator. cal_file = 'cal-files/24dB-atten-48-0007-Det3-100-6000MHz.json' try: pwrmeter = rpyc.connect("127.0.0.1", 18863) except ConnectionRefusedError: print("Can't connect to the pwrmeter app. Is it running?") sys.exit(-1) pwrmeter.root.initialize() pwr_detector = 0 cal_file_path = str(pwr_app_path / cal_file) print(f'{cal_file_path=}') pwrmeter.root.detectors[pwr_detector].load_caldata(cal_file_path) pwrmeter.root.detectors[pwr_detector].apply_correction = True # Disable the second detector pwrmeter.root.detector_enable(1, False)
-
Measure output power as a function of frequency.
<<max-linear-gains>> def measure_max_linear_pwr(rfgen, pwrmeter, det, freq_list): sig_pwr = {} plo = rfgen.root.plo_chan for f in freq_list: plo.plo_ctl.freq = f buf_gain = max_linear_gain(f) plo.plo_ctl.buffer_gain = int(buf_gain) rfgen.root.configure_plo() pwrmeter.root.detectors[det].freq = f pwrmeter.root.measure(det) pwr = pwrmeter.root.detectors[det].pwr sleep(0.2) sig_pwr['{:.1f}'.format(f)] = float(pwr) return sig_pwr def measure_integrated_pwr(rfgen, pwrmeter, det, freq_list): sig_pwr = {} plo = rfgen.root.plo_chan for f in freq_list: plo.plo_ctl.freq = f try: rfgen.root.configure_plo_freq() except TimeoutError as te: # Retry print(te) rfgen.root.configure_plo_freq() pwrmeter.root.detectors[det].freq = f pwrmeter.root.measure(det) try: pwr = pwrmeter.root.detectors[det].pwr except TimeoutError as te: # Retry print(te) pwr = pwrmeter.root.detectors[det].pwr sleep(0.3) sig_pwr['{:.1f}'.format(f)] = float(pwr) return sig_pwr
linear_gains = { 25: hmc833.OutputBufferGain.MAXGAIN, 150: hmc833.OutputBufferGain.MAXGAIN_MINUS_3DB, 200: hmc833.OutputBufferGain.MAXGAIN_MINUS_6DB, 1200: hmc833.OutputBufferGain.MAXGAIN_MINUS_3DB, 1500: hmc833.OutputBufferGain.MAXGAIN_MINUS_6DB, 2000: hmc833.OutputBufferGain.MAXGAIN_MINUS_3DB, 3000: hmc833.OutputBufferGain.MAXGAIN, 6000: hmc833.OutputBufferGain.MAXGAIN } def max_linear_gain(f): i = 0 freqs = list(linear_gains.keys()) while i < len(freqs): if f > freqs[i]: i += 1 else: k = max(0, i-1) gain = list(linear_gains.values())[k] break return gain
-
Measure output power for each gain setting.
def main(): defaultOutputFile = 'rfgen-output-power.json' parser = ArgumentParser(description= '''Calibrate low spurious RF signal generator''') parser.add_argument( "-O", "--output_file", default=defaultOutputFile, help=f"File to write measured output powers. " f"Default: {defaultOutputFile}" ) parser.add_argument( "-M", "--max_linear_gain", action='store_true', help="Measure output power for maximum linear gain settings." ) args = parser.parse_args() <<initialize-rfgen>> <<initialize-pwrmeter>> # Insert more cal. points in and around areas of abrupt power # level changes. #freq_list = [float(f) for f in np.linspace(100.0, 6000.0, 100).round()] freq_list = [ 100., 160., 219., 279., 338., 400., 458., 517., 577., 636., 696., 756., 815., 875., 934., 994., 1054., 1113., 1173., 1233., 1292., 1352., 1411., 1471., 1530., 1590., 1649., 1709., 1769., 1828., 1888., 1950., 2007., 2067., 2126., 2186., 2245., 2305., 2365., 2424., 2484., 2543., 2603., 2663., 2722., 2782., 2841., 2901., 2961., 3020., 3080., 3139., 3200., 3259., 3318., 3378., 3440., 3497., 3557., 3616., 3676., 3735., 3795., 3855., 3914., 3974., 4033., 4093., 4153., 4212., 4272., 4331., 4391., 4451., 4510., 4570., 4629., 4689., 4748., 4808., 4868., 4920., 4987., 5046., 5106., 5166., 5225., 5285., 5344., 5404., 5464., 5523., 5583., 5642., 5702., 5762., 5821., 5881., 5940., 6000.] freq_list.extend([1442, 1452, 1462, 1472, 1480, 1499, 1500, 1512, 1522, 1532, 1542, 1550, 1572, 1582, 1592]) freq_list.extend([2945, 2957, 2967, 2975, 2985, 3000, 3001, 3015, 3025, 3035, 3045]) freq_list.sort() divider_gain = hmc833.DividerGain.MAXGAIN_MINUS_3DB buffer_gain_settings = { 'max-minus-9dB': hmc833.OutputBufferGain.MAXGAIN_MINUS_9DB, 'max-minus-6dB': hmc833.OutputBufferGain.MAXGAIN_MINUS_6DB, 'max-minus-3dB': hmc833.OutputBufferGain.MAXGAIN_MINUS_3DB, 'maxgain': hmc833.OutputBufferGain.MAXGAIN} plo = rfgen.root.plo_chan plo.plo_ctl.divider_gain = divider_gain rfgen.root.configure_plo() if args.max_linear_gain is True: output_pwr = { "linear_gains": linear_gains, } output_pwr['pwr'] = measure_max_linear_pwr( rfgen, pwrmeter, pwr_detector, freq_list) else: output_pwr = {} for label, gain in buffer_gain_settings.items(): print(f'{label=}, {gain=}') plo.plo_ctl.buffer_gain = gain rfgen.root.configure_plo() output_pwr[label] = measure_integrated_pwr( rfgen, pwrmeter, pwr_detector, freq_list) with open(args.output_file, 'w') as fd: json.dump(output_pwr, fd) plo.plo_ctl.vco_mute = True rfgen.root.set_calibration_mode(False) rfgen.close()
Format measured calibration data
import json from argparse import ArgumentParser import numpy as np def format_cal_data_dict(cd_dict): cols = 4 sd = [f'{f}: {float(p):.2f},' for f, p in cd_dict.items()] output_str = '\n'.join([''.join([' '] + [f'{ls: <16}' for ls in lst[:-1]] + [f'{lst[-1]}']) for lst in [sd[i:i+cols] for i in range(0, len(sd), cols)]]) return output_str def format_chan_cal_data(chan_dict): output_str = '\n'.join([f" '{k}': {{\n{format_cal_data_dict(cd_dict)}\n }}," for k, cd_dict in chan_dict.items()]) return output_str def read_cal_data(data_files): with open(data_files[0]) as fd: cal_data = json.load(fd) if len(data_files) > 1: # Read all the files and generate averages for the # measured signal powers. cal_data_list = [cal_data] for data_file in data_files[1:]: with open(data_file) as fd: cal_data_list.append(json.load(fd)) chan_arrays = {} for data in cal_data_list: for chan_id, chan_dict in data.items(): if chan_id in chan_arrays: pwr_arrays = chan_arrays[chan_id] else: pwr_arrays = {} chan_arrays[chan_id] = pwr_arrays for gain_label, cd_dict in chan_dict.items(): parr = np.array([p for p in cd_dict.values()]) if gain_label in pwr_arrays: pwr_arrays[gain_label] += parr else: pwr_arrays[gain_label] = parr for chan_id, chan_array in chan_arrays.items(): for gain_label, pwr_array in chan_array.items(): # Replace pwr values in cal_data with the averages # computed from pwr_array parr = chan_arrays[chan_id][gain_label] / len(data_files) cal_data[chan_id][gain_label] = { fs: p for fs, p in zip(cal_data[chan_id][gain_label], parr)} return cal_data def main(cal_data_files): cal_data = read_cal_data(cal_data_files) print('CHAN_CAL_DATA = {') print(format_chan_cal_data(cal_data)) print('}') if __name__ == '__main__': defaultInputFile = 'rfgen-output-power.json' parser = ArgumentParser(description= '''Format RF signal generator calibration data''') parser.add_argument( "-I", "--input_files", default=[defaultInputFile], nargs='+', help=f"File containing calibration data as written by" " the rfgen-calibrate.py script." f" Default: {defaultInputFile}" ) args = parser.parse_args() main(args.input_files)